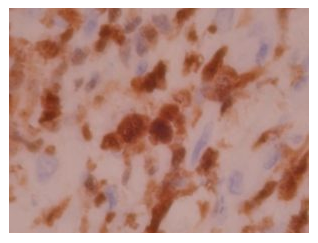
ALK-1 by IHC
ALK-1 by IHC-12376 - Technical only, 12379 - Technical & interpretation
ALK-1 by IHC
12376 - Technical only, 12379 - Technical & interpretation
LAB12482
LAB12379
LAB12379
ALK1
IHC
IHC
- All IHC stains will include a positive control tissue
- The majority of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma are positive for ALK-1. The reported positively rate varies from <15% to >67%
- ALK-1 also can be seen in a subset of Large B Cell Lymphomas (cytoplasmic only staining)
- Hodgkin’s Disease does not react with ALK-1
- Recent data suggests favorable prognostic significance associated with ALK expression (10 yr. Survival rate of 78.5% for ALK positive cases vs. 44.4% survival for ALK negative cases). ALK expression also correlates with young patient age and low stage disease
- ALK expression is also seen in most (60%) inflammatory myo-fibroblastic tumors
Tissue
Submit a formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded tissue block
Formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissue block
Tissue section mounted on a charged, unstained slide
Ambient (preferred)
AHL - Immunohistochemistry
Mo - Fr
1 - 2 days
Immunohistochemical staining and microscopic examination
If requested, an interpretive report will be provided
Specifications
- A monoclonal antibody that recognizes a specific tyrosine kinase receptor, formed by the t(2,5) translocation called anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)
- The t(2,5) translocation forms a truncated protein NPM-ALK or p80, which is found in many cases of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (nuclear, nucleolar, and cytoplasmic staining)
- Rare cases of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma associated with trans-locations involving 2 p23 but genes other than NPM also express this antibody (cytoplasmic restricted staining)
- A new type of Large B Cell Lymphoma recently described can express the full length ALK protein (cytoplasmic staining)
- ALK-1 does not label normal lymphoid tissue
- Rare reactivity with CNS system to ALK has been detected on frozen sections
Staining patterns
- Most Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphomas show cytoplasmic, nuclear, and often nucleolar staining (80% of cases)
- Rare cases of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma without NPM protein expression show cytoplasmic staining only (since the ALK associated protein is not trans-located to the nucleus)
- A recently described subset of Large B Cell Lymphomas (lack t(2,5) and CD 30) exhibit cytoplasmic staining and express the full length ALK protein
References
- Benharroch D, et al. ALK-Positive Lymphomas, a Single Disease with a Broad Spectrum of Morphology. Blood, Vol. 91, No. 6, 2076-2084, 1998.
- Pittaluga S, et al. The Monoclonal Antibody ALK-1, Identifies a Distinct Morphological Subytpe of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Associated with 2p23/ALK Rearrangements. Am J Path 151: 343-351, 1997.
- Delsol G, et al. A New Subtype of Large B Cell Lymphoma Expressing the ALK Kinase and lacking the 2;5 Translocation. Blood, Vol. 89, No. 5, 1483-1490, 1997.
- Pulford K, et al. Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) and Nucleolar Protein Nucleophosmin (NPM) – ALK Proteins in Normal and Neoplastic Cells. The Monoclonal Antibody ALK-1. Blood, Vol. 89, No. 4, 1394-1404, 1997.
- Chan, John: Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: Redefining its Morphologic Spectrum and Importance of Recognition of the ALK-Positive Subset. Blood, Vol. 91, 2076-84, 1998.
- Cook, JR et al. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) expressions in the inflammatory Myo-fibroblastic tumor; a comparative Immunohistochemical study. Am J Surg Pathol 25(11): 1364-1371, 2001.
88342 - 1st stain
88341 - each additional stain
88341 - each additional stain
03/02/2016
10/17/2018
10/02/2020