Lyme disease serology, polyvalent with reflex-659
Test info
OspC
B. mayonii
B. afzelii
B. garinii
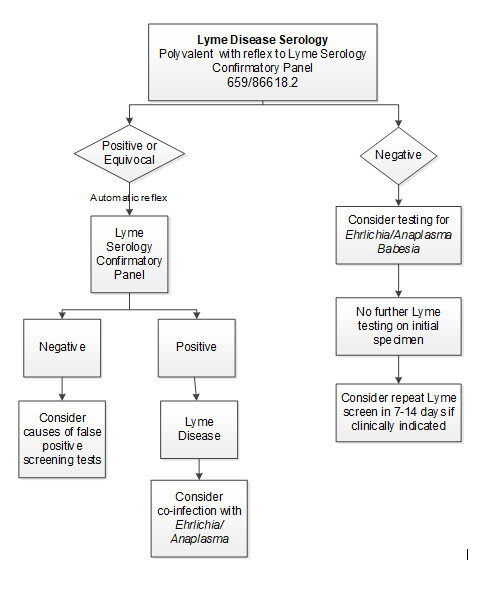
Positive results will reflex to Lyme serology confirmatory panel
Negative results may occur in patients recently infected (≤14 days) with B. burgdorferi.
If recent infection is suspected, repeat testing on a new sample collected in 7-14 days is recommended.
Specimen
Immediately following collection, thoroughly mix sample by gently inverting 5 times
- Allow sample to clot for a minimum of 30 minutes
- Spin within two (2) hours of sample collection
Gold serum separator (SST) tube
- Allow sample to clot
- Spin
- Transfer serum to a False bottom plasma/serum transport vial/tube (AHL), labelled as serum, within two (2) hours of sample collection
Refrigerated (preferred) - 7 days
Frozen (OK) - 3 months
- Improper labels (unlabeled or mislabeled)
- Hemolysis (some procedures)
- Improper anticoagulant or ratio
- Delay in transport
- Improper storage temperature affecting results
- Improper container
- Leaking container resulting in compromised specimen
- Quantity not sufficient (QNS)
Performance
Indirect Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLIA)
Clinical and Interpretive info
Negative
Negative results may occur in patients recently infected (≤14 days) with B. burgdorferi. If recent infection is suspected, repeat testing on a new sample collected in 7–14 days is recommended.
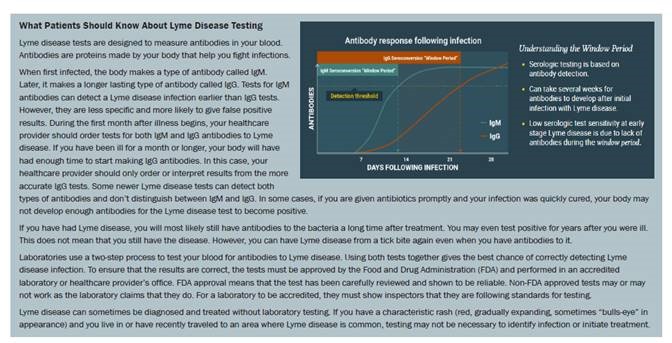
IgM immunoassay results should only be considered as indicative of recent infections in patients presenting within 30 days of symptom onset. Consideration of IgM immunoblot results in patients with symptoms lasting >30 days is discouraged due to the risk of false positive IgM immunoblot results or prolonged IgM seropositivity following disease resolution.
Testing of a new specimen collected in 7–14 days to demonstrate IgG seroconversion may be considered to confirm infection. If both tests are equivocal consider repeat testing in 7-14 days if clinically warranted.
Timing of infection (acute/recent vs. past) cannot be determined by these assays. Clinical correlation is required
Results should not be used to monitor or establish adequate response to therapy. Response to therapy is confirmed through resolution of clinical symptoms; additional laboratory testing should not be performed. If both screening and confirmatory tests are equivocal consider repeat testing in 7–14 days if clinically warranted.
Positive Lyme Serology Confirmatory Panel and Neurological Symptoms
- Order Lyme antibody testing on CSF
- Consider PCR testing (low sensitivity, negative results do not exclude neuroborreliosis)
Positive Lyme Serology Confirmatory Panel and Knee effusion
- Lyme disease serologies are used to establish the diagnosis of Lyme arthritis in patients with potential exposure to Ixodes ticks and signs and symptoms of Lyme arthritis
- All patients with Lyme arthritis will have positive serologies for B. burgdorferi since Lyme arthritis is a late manifestation
- Synovial fluid testing can establish the presence of an inflammatory arthritis, characterized by mean synovial WBC counts of 10,000-25,000 cells/µL
- Analysis of synovial fluid by ELISA or Lyme serology confirmatory panel will also demonstrate B. burgdorferi reactivity, but such testing is unnecessary, since it is neither more sensitive nor more specific than serum analysis.
- Consider PCR testing on synovial fluid (relatively good sensitivity by negative results do not exclude Lyme arthritis)
- PCR testing of synovial fluid has not been validated for widespread clinical use
Billing
Additional CPT codes (if appropriate)
86617 x 2 - Western Blot