Treponema pallidum-8325
Test info
Trep
T pallidum
VDRL
RPR
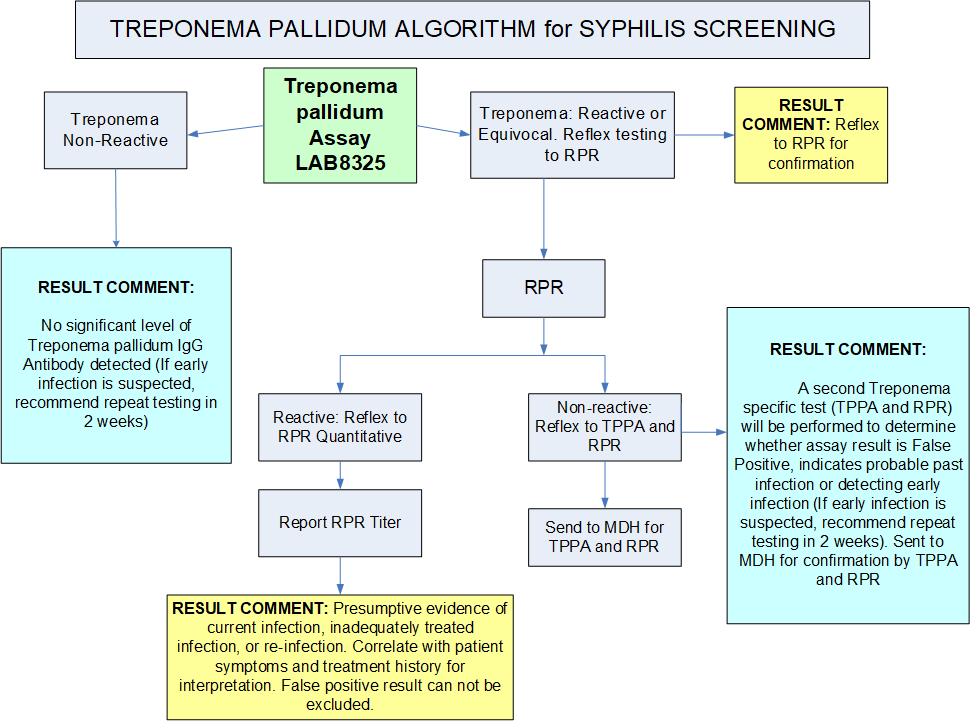
- All reactive results reflex to an RPR
- If the RPR is positive, an RPR (Quant) Titer will be performed
at an additional charge. - If the RPR titer is non-reactive, the specimen is referred to the Minnesota Department of Health (MDH) for confirmation by TPPA (Treponema pallidum particle agglutination) and RPR (Rapid Plasma Reagin) assay
- If the RPR is positive, an RPR (Quant) Titer will be performed
Treponema pallidum is the causative agent of syphilis, a chronic infection with many clinical manifestations which occur in distinct stages.
Testing not indicated for patients <6 months old. See Infant RPR (LAB14248).
Specimen
Immediately following collection, mix sample by gently inverting 5 times
- Allow sample to clot for a minimum of 30 minutes
- Spin within two (2) hours of sample collection
Gold serum separator (SST) tube
- Allow sample to clot
- Spin
- Transfer serum to a False bottom plasma/serum transport vial/tube (AHL), labelled as serum, within two (2) hours of sample collection
Refrigerated (preferred) - 14 days
Ambient - 7 days
Frozen - 12 months
- Gross hemolysis
- Lipemic samples
- Samples exhibiting obvious microbial contamination
- Heat inactivated samples
- CSF or cord blood
- Improper labels (unlabeled or mislabeled)
- Improper anticoagulant or ratio
- Delay in transport
- Improper storage temperature affecting results
- Improper container
- Leaking container resulting in compromised specimen
- Quantity not sufficient (QNS)
- Patient <6 months old
Performance
Chemiluminescent immunoassay (CLIA)
Clinical and Interpretive info
Non-reactive
Clinical consultation
The Minnesota Department of Health (MDH) provides a Syphilis Hotline for clinician questions about syphilis testing, results interpretation, treatment, and followup. Please call (651) 201-4024 to speak with an MDH clinical expert.
Treponema pallidum algorithm for Syphilis screening
Treponema pallidum is the causative agent of syphilis, a chronic infection with many clinical manifestations which occur in distinct stages.
- Primary Stage: The time between infection with syphilis and the start of the first symptoms can range from 10 to 90 days (average 21), usually marked by the appearance of a single (or multiple) sore called a chancre. The chancre appears at the spot where syphilis entered the body and lasts 3 to 6 weeks; it will heal on its own. If adequate treatment is not administered, the infection will progress to the secondary stage.
- Secondary Stage: The second stage starts when one or more areas of the skin break into a rash that usually does not itch. Rashes can appear as the chancre is fading or can be delayed for weeks. The rash often appears as rough, red or reddish brown spots both on the palms of the hands and bottoms of the feet. Rashes will clear up on their own even without treatment. Other symptoms can include fever, headaches, weight loss, muscle aches and tiredness.
- Late (Tertiary) Syphilis: The latent (hidden) stage begins when the secondary symptoms disappear. Without treatment syphilis may begin to damage the internal organs, including the brain, nerves, eyes, heart, blood vessels, liver, bones, and joints. This internal damage may show up many years later or in the tertiary stage of syphilis. Late stage signs and symptoms include paralysis, numbness, gradual blindness, and dementia and may cause death.The diagnosis of syphilis should not be made on a single reactive result without the support of a positive patient history or other clinical evidence. Non-treponemal tests (RPR & VDRL) when quantitated may be used to indicate a response to therapy. With cardiolipin type antigens, biologic false positive reactions have been reported in diseases such as infectious and viral pneumonia. Several reports indicated the occurrence of false positive reactions in pregnancy, narcotic addiction, and auto-immune diseases.
Syphilis can be transmitted to the fetus resulting in stillbirth or death shortly after birth. If left untreated, the baby may become developmentally delayed, have seizures or die.
The diagnosis of syphilis should not be made on a single reactive result without the support of a positive patient history or other clinical evidence. Non-treponemal tests (RPR & VDRL) when quantitated may be used to indicate a response to therapy. With cardiolipin type antigens, biologic false positive reactions have been reported in diseases such as infectious and viral pneumonia. Several reports indicated the occurrence of false positive reactions in pregnancy, narcotic addiction, and auto-immune diseases.
Billing
Additional CPT codes (if appropriate):
86592 - Rapid plasma reagin (RPR)
86593 - RPR quant
86780 - Treponema pallidum particle agglutination (TPPA)
86592 - Unheated serum reagin (USR)