BAP1 by IHC
BAP1 by IHC-12376 - Technical only, 12379 - Technical & interpretation
LAB12379
All IHC stains will include a positive control tissue
Submit formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissue block
FFPE tissue block
Tissue section mounted on a charged, unstained slide
Ambient (preferred)
- Unlabeled/mislabeled
- Insufficient tissue
- Slides broken beyond repair
Immunohistochemical staining and microscopic examination
If requested, an interpretive report will be provided
Specifications
BAP1 is a tumor suppressor protein frequently lost in mesotheliomas and in other malignant neoplasms including melanomas and carcinomas. Renal cell carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma show frequent nuclear loss of BAP1. Loss of BAP1 nuclear staining has also been reported in other carcinomas including lung non-small cell carcinomas and breast cancer.
Staining pattern
- Loss of nuclear BAP1 staining in a population of tumor cells defined by IHC as mesothelial in origin is diagnostic of malignant mesothelioma.
- Intact nuclear staining is mesothelial cells does not rule out malignant mesothelioma. Consider additional testing (MTAP IHC, p16 FISH testing).
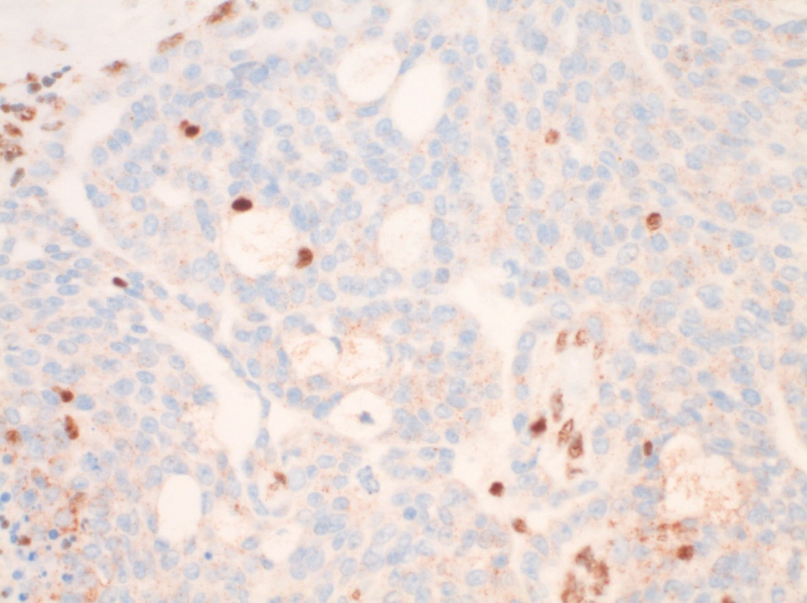
Applications
- Loss of nuclear BAP1 staining can be used to differentiate mesothelioma from reactive mesothelial proliferations. Mesothelial origin should be first established using a a panel of IHC markers (WT-1, D240, Calretinin, MOC31, Claudin-4, etc.).
- Loss of nuclear BAP1 staining by immunohistochemistry is highly concordant with BAP1 mutation, with a reported specificity of 100%.
- Reported overall BAP1 sensitivity for pleural mesotheliomas is 50-65%. Reported sensitivity for mesothelioma subtypes: 61-77% for epithelioid mesothelioma, 33-49% for biphasic malignant mesothelioma, 0-22% for sarcomatoid mesothelioma. Reported sensitivity for peritoneal mesothelioma is estimated to be 55-67%
References
- Hwang HC et al. BAP1 Immunohistochemistry and p16 FISH in the Diagnosis of Sarcomatous and Desmoplastic Mesotheliomas. Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40(5):714-8.
- Hwang HC et al. Utility of BAP1 Immunohistochemistry and p16 (CDKN2A) FISH in the Diagnosis of Malignant Mesothelioma in Effusion Cytology Specimens. Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:120–126.
- Cigognetti M et al. BAP1 (BRCA1-associated protein 1) is a highly specific marker for differentiating mesothelioma from reactive mesothelial proliferations. Modern Pathology 2015;28:1043–1057.
- Andrici J et al. Loss of expression of BAP1 is a useful adjunct, which strongly supports the diagnosis of mesothelioma in effusion cytology. Modern Pathology 2015; 28(10):1360-8.
- Chapel DB et al. Application of immunohistochemistry in diagnosis and management of malignant mesothelioma. Transl Lung Cancer Res 2020;9 (Suppl 1): S3-S27.
88341 - each additional stain