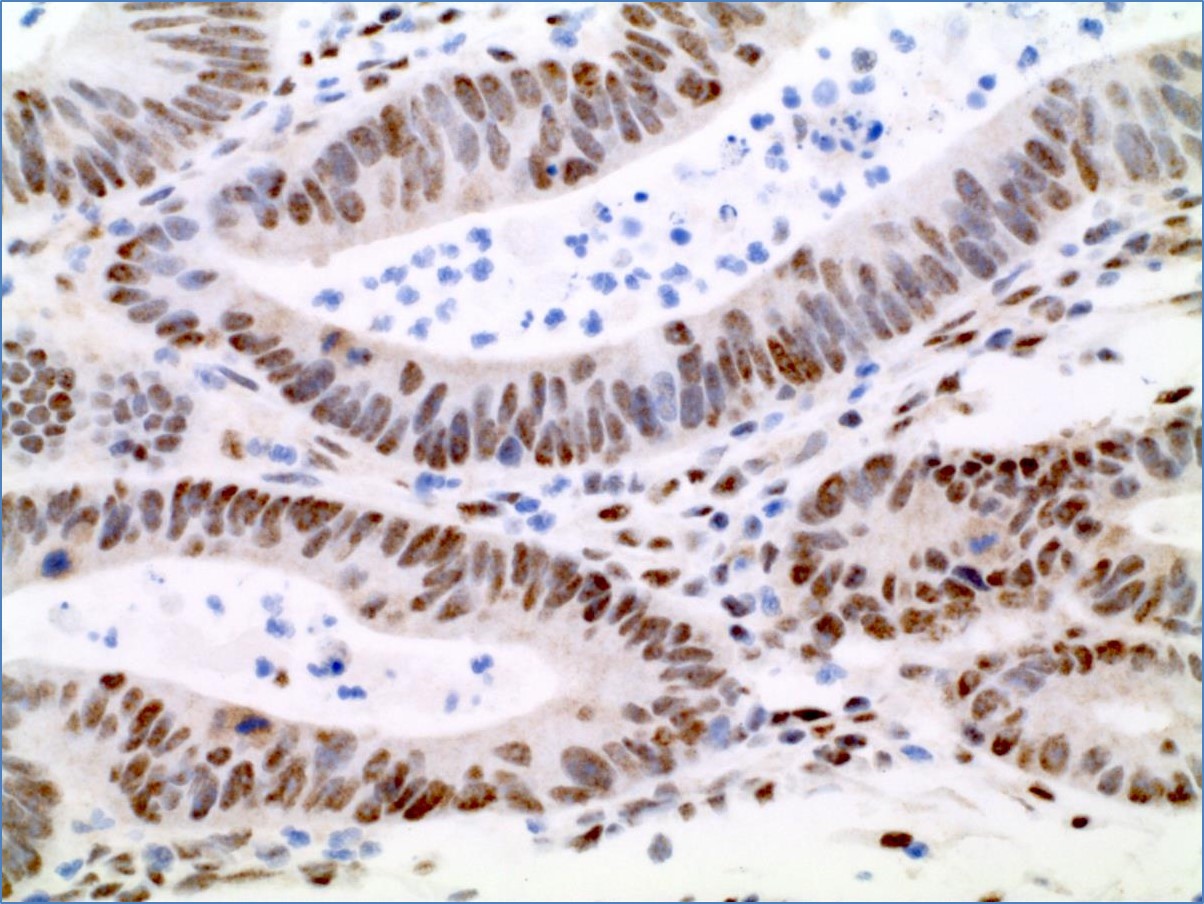
MLH1 by IHC
MLH1 by IHC-12376 - Technical only, 12379 - Technical & interpretation
MLH1 by IHC
12376 - Technical only, 12379 - Technical & interpretation
LAB12376
LAB12379
LAB12379
Microsatellite instability marker
- All IHC stains will include a positive control tissue
- Used in a panel to identify patients at high risk for having hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), also known as Lynch syndrome
- IHC analysis is helpful for identifying the gene(s) responsible for the defective DNA mismatch repair within the tumor; the majority of MSI-H tumors show a loss of expression of at least 1 of the 4 mismatch repair genes
- MSI-H phenotype or loss of protein expression by IHC within a tumor does not distinguish between somatic and germline mutations. Genetic testing of the gene indicated by IHC analysis can help to distinguish between these 2 possibilities
Tissue
Submit a formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue block
FFPE tissue block
FFPE tissue section mounted on a charged, unstained slide
Ambient (preferred)
- Unlabeled/mislabeled block
- Insufficient tissue
- Slides broken beyond repair
AHL - Immunohistochemistry
Mo - Fr
1 - 2 days
Immunohistochemical staining and microscopic examination
If requested, an interpretive report will be provided
Specifications
- Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), also known as Lynch syndrome, is an autosomal dominant hereditary cancer syndrome associated with germline mutations in the mismatch repair genes: MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2
- Patients with HNPCC have an increased risk of developing colorectal and endometrial cancer
Staining pattern
- Nuclear staining of internal control lymphocytes, and MLH1 intact tumor cells
- Absence of staining for MLH1 in tumor nuclei indicates loss of protein expression for this marker
References
- Burgart LJ: Testing for defective DNA mismatch repair in colorectal carcinoma. A practical guide. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:1385-1389.
88342 - 1st stain
88341 - each additional stain
88341 - each additional stain
10/30/2017
10/19/2018
01/21/2026