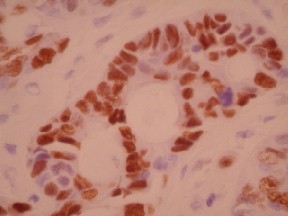
p57 by IHC
p57 by IHC-12376 - Technical only, 12379 - Technical & interpretation
LAB12379
- All IHC stains will include a positive control tissue
- P57 staining in intervillous trophoblastic islands, in the absence of staining in villous mesenchyme and cyto-trophoblastic cells is diagnostic for hydatidiform mole (note: focal/rare staining of P57 in cyto-trophoblastic cells is considered negative)
- P57 staining of cytotrophoblast, villous mesenchyme, and intervillous trophoblastic islands is seen in spontaneous abortion (hydropic) or partial hydatidiform mole; to distinguish these two entities, flow cytometry is needed (hydropic POC is diploid; partial hydatidiform mole is triploid)
Submit a formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded tissue block
Formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissue block
FFPE tissue section mounted on a charged, unstained slide
Ambient (preferred)
- Unlabeled/mislabeled block
- Insufficient tissue
- Slides broken beyond repair
Immunohistochemical staining and microscopic examination
If requested, an interpretive report will be provided
Specifications
- P57 is a cell cycle inhibitor and tumor suppressor, which is encoded by a maternally imprinted gene
- P57 is a negative regulator of cell proliferation
- This antibody is useful in distinguishing complete hydatidiform moles from other types of hydropic conceptuses (including hydropic/spontaneous abortuses and partial hydatidiform moles)
Comments
If complete hydatidiform mole is present:
Microscopic sections show variably sized villi, virtually all of which are swollen and enlarged with cerebriform contours and cleft-like cisternae, associated with prominent intervillous trophoblastic proliferation. The morphology is quite suggestive of a molar pregnancy. Immunohistochemistry stains for P57 antigen are performed and are negative in the villous mesenchyme and cytotrophoblast, with appropriate positive staining in the intervillous trophoblastic islands, confirming the diagnosis of complete hydatidiform mole. Thus, careful follow up with serial serum HCG levels is recommended to ensure that the levels return to normal.
These results are discussed with Dr. ____ and the report is faxed on _____/
or
If the differential is between spontaneous abortion and partial hydatidiform mole:
Microscopic sections show swollen villi with a mild degree of trophoblastic proliferation. A P57 immunohistochemical stain is performed, to exclude the possibility of a complete hydatidiform mole. This stain shows positive staining within cytotrophoblast, villous mesenchyme, and intervillous trophoblastic islands, excluding the possibility of a complete hydatidiform mole. Thus, the differential diagnosis of this case includes a spontaneous abortion with hydropic changes vs. a partial hydatidiform mole. Therefore, a paraffin block will be submitted for flow cytometry studies to determine whether or not this tissue is diploid (hydropic POC) or triploid (partial hydatidiform mole). The final diagnosis will be deferred pending the flow cytometry studies. An addendum report will follow.
Staining pattern
- Nuclear based staining
- The determination of the type of cells that are staining for this marker is crucial for interpretation (i.e. cytotrophoblast, vs. villous mesenchyme, vs. intervillous trophoblastic island staining)
References
- Castrillon DH et al: Discrimination of complete hydatidiform mole from its mimics by immunohistochemistry of the paternally imprinted gene product P57. Am J Surg Pathol 25(10): 1225-1230, 2001.
88341 - each additional stain