Bilirubin, total
Bilirubin, total-46
Total bilirubin is the sum of the unconjugated and conjugated fractions and is elevated in conditions causing hepatic obstruction, hepatitis, cirrhosis, hemolytic disorders, and several inherited enzyme deficiencies.
Immediately following collection, mix sample thoroughly by gently inverting 8 - 10, times to prevent clotting
- Spin within two (2) hours of sample collection
- Protect specimen from light. Exposure to direct sunlight can decrease bilirubin in samples by 50% within one hour.
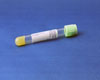
Lt green plasma separator (PST)
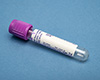
EDTA plasma
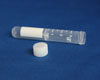
Gold serum separator (SST) tube
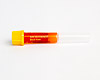
Microtainer - amber serum separator (SST), with extender
Neonatal bilirubin samples should be collected into an amber microtainer. If no amber microtainer is available, samples should be protected from light by wrapping in aluminum foil during transport to the testing facility
Gold:
Immediatley following collection, mix sample by gently inverting 5 times
EDTA:
Immediatley following collection, mix sample by gently inverting 5 times
Gold:
- Allow sample to clot for a minimum of 30 minutes
- Spin within two (2) hours of sample collection
EDTA
- Spin
- Transfer plasma to a False bottom plasma/serum transport vial/tube (AHL), labeled as EDTA plasma, within two (2) hours of sample collection
Gold serum separator (SST) tube
or
Microtainer - amber serum separator (SST), with extender, in a Snap cap conical vial/tube,
or
False bottom plasma/serum transport vial/tube (AHL)
Refrigerated - 7 days
Ambient - 1 day
Frozen - 6 months
- Improper labels (unlabeled or mislabeled)
- Hemolysis (some procedures)
- Improper anticoagulant or ratio
- Delay in transport
- Improper storage temperature affecting results
- Improper container
- Leaking container resulting in compromised specimen
- Quantity not sufficient (QNS)
Endpoint Colorimetric with Diazo
| Age | Range |
| Adult | 0 - 1.2 mg/dL |
| 0 - 2 days | < 7.0 mg/dL |
| 3 - 5 days | < 6.0 mg/dL |
| 6 - 30 days | < 4.0 mg/dL |
| 31 days - 18 years | 0 - 1.2 mg/dL |
<17 yrs: > 14.9 mg/dL
Red blood cells at the end of their circulating life are broken down in the reticuloendothelial system, mainly the spleen. The resulting heme, once the iron is removed, is then converted to bilirubin. This process accounts for about 80% of the 500 μmol (300 mg) of bilirubin formed daily. Other sources of bilirubin include the breakdown of myoglobin and cytochromes and the catabolism of immature red blood cells in the bone marrow.
Once formed, bilirubin is transported to the liver bound to albumin. This fraction of bilirubin is referred to as indirect or unconjugated bilirubin. In the liver, bilirubin is conjugated to glucuronic acid (mono- and di- glucuronides) to form conjugated bilirubin by the enzyme uridyl diphosphate glucuronyl transferase. Conjugated bilirubin or direct bilirubin is excreted via the biliary system into the intestine, where it is metabolized by bacteria to a group of products known collectively as stercobilinogen. Elimination is almost complete and serum levels are normally negligible.
Total bilirubin is the sum of the unconjugated and conjugated fractions. Total bilirubin is elevated in conditions causing hepatic obstruction, hepatitis, cirrhosis, hemolytic disorders, and several inherited enzyme deficiencies.