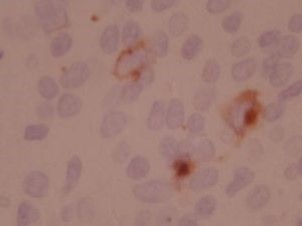
Epstein-Barr Virus in situ hybridization (ISH)
Epstein-Barr Virus in situ hybridization (ISH)-12376 - Technical only, 12379 - Technical & interpretation
LAB12379
EBV in situ hybridization
EBV ISH
- All ISH stains will include a positive control tissue
- EBV is a member of Herpes virus family, and is the causative agent in infectious mononucleosis EBV is associated with some cases of Hodgkin's disease, Burkitt's lymphoma, peripheral T-cell lymphoma, gastric carcinoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma EBV is also associated with post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTIPD)
- The EBV in situ test is much more sensitive than the EBV IHC test
Submit a formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded tissue block
Formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissue block
FFPE tissue section mounted on a charged, unstained slide
Ambient (preferred)
- Unlabeled/mislabeled block
- Insufficient tissue
- Slides broken beyond repair
In situ hybridization and microscopic examination
If requested, an interpretive report will be provided
Probe
EBV (EBER; Epstein-Barr Virus Early RNA)+R40 RNA probe
Specifications
Recognizes early RNA transcript of EBV infection The RNA transcript accumulates in nuclei of actively infected cells
Staining pattern
- Nuclear
References
1. Ambinder RF et al: Epstein-Barr-encoded RNA in situ hybridization: diagnostic applications. Human Pathol 25:602-605, 1994.
2. Randhawa P.S et al: Recurrent Epstein-Barr virus-associated lesions in organ transplant recipients. Hum Pathol. Feb;27(2):157-64. 1996.
88364 - each additional stain