RSV by NAAT
RSV by NAAT-14483
RSV test
Patients presenting with symptoms for Respiratory syncytial viral infection
Please have patient blow their nose prior to NP and nasal collections. Excessive mucus is known inhibitor/interfering substance for molecular testing.
For Allina Health Clinic Ambulatory patients only:
RespDirect (Enhanced Direct Load Tube)
For all other patients:
Universal Transport media (UTM)
For Allina Health Clinic Ambulatory patients:
Nasal collection
Note: Swab included in RespDirect (Enhanced Direct Load Tube) kit is also acceptable for nasopharyngeal collections. See NP collection instructions below.
- Insert swab in one nostril 1/2”-3/4” until swab tip is no longer visible.
- Rotate the swab using moderate pressure along the nostril wall at least 4 times.
- Complete the collection by swabbing the other nostril in the same fashion.
- Uncap the transport media, insert the swab into the media, break swab against the tube at the score line, recap.
For all other patients:
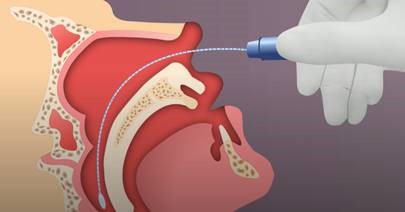
Nasopharyngeal (NP) swab collection:
Use the mini-tip NP swab included in the UTM packaging.
- Tip the patient’s head back.
- Gently insert the NP swab into the nostril parallel to the palate (not upwards) until resistance is encountered or the distance is equivalent to that from the ear to the nostril of the patient, indicating contact with the nasopharynx.
- If any resistance is met in the passageways, do not force the swab; back off and try reinserting it at a different angle, closer to the floor of the nasal canal, or try the other nostril.
- Gently rub and roll the swab for 10-15 seconds while the swab is in contact with the nasopharyngeal wall.
- The CDC recommends leaving the swab in place for several seconds to absorb secretions.
- Slowly remove the swab and place in the transport medium.
- Break the swab shaft so that it fits into the medium container and recap tightly.
- Label the specimen appropriately. Document the source “NP” on the label.
New England Journal of Medicine video on NP swab collection: Nasopharyngeal Swab Collection Video
RespDirect (Enhanced Direct Load Tube) - Allina Health Clinic Ambulatory Patients only
Universal Transport media (UTM)
Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS)
Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS)
RespDirect (Enhanced Direct Load Tube) - Allina Health Clinic Ambulatory Patients only
- Refrigerated - 6 days
- Ambient - 6 days
Universal Transport media (UTM)
- Refrigerated (2-8°C) – 7 days
- Improper label (unlabeled or mislabeled)
- Oropharyngeal specimens
- Specimens types, swabs, and/or collection containers other than listed above.
- Specimens that do not meet listed transport and stability above.
- Leaking container
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
Negative
Excessive mucus is a known inhibitor/interfering substance for molecular tests. Review specimen tab for patient preparation.